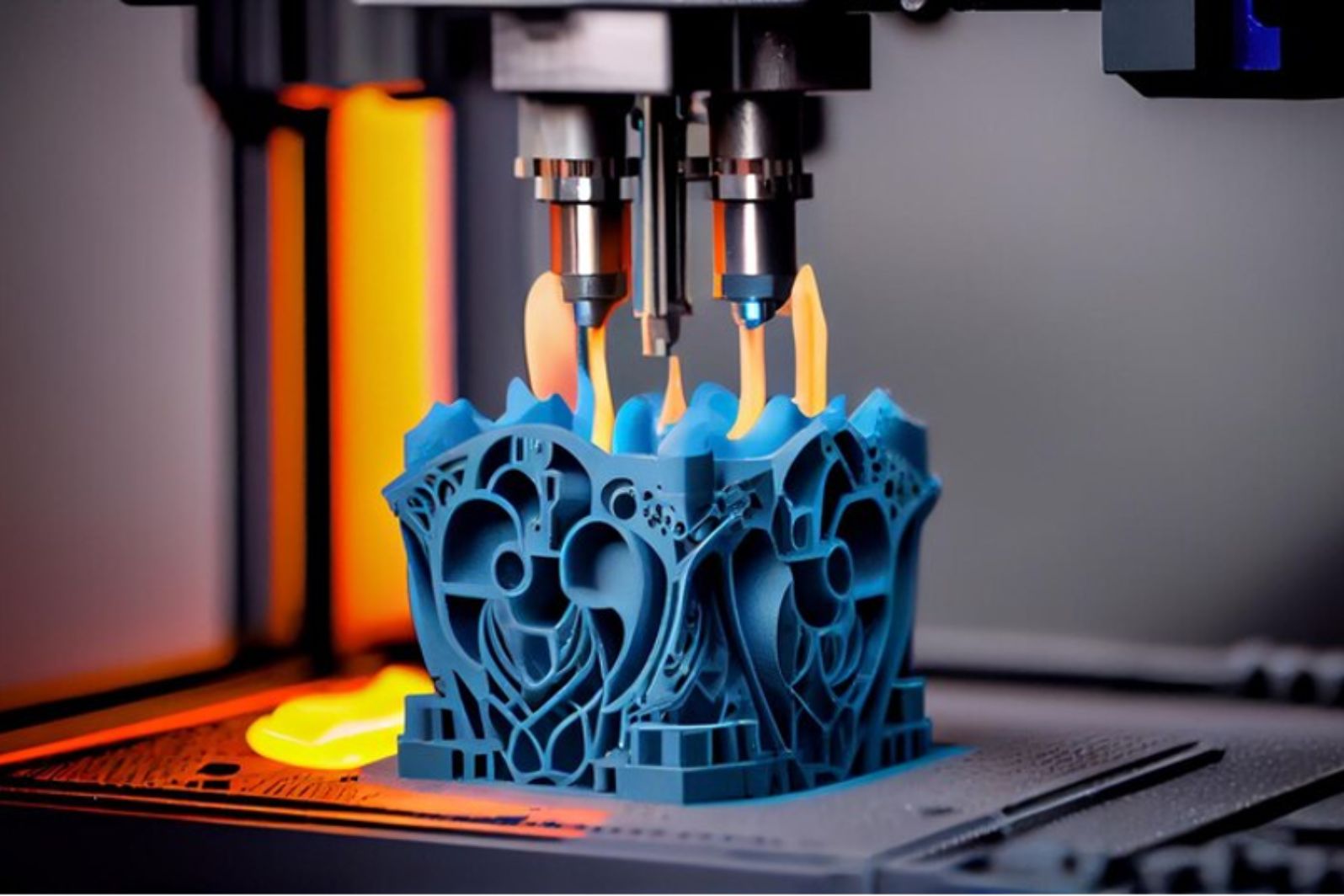
In recent years, the manufacturing landscape has witnessed a revolutionary shift propelled by the emergence of 3D printing. Also known as additive manufacturing, this groundbreaking technology has transcended its initial applications and is reshaping industries, economies, and the very essence of production.
The Essence of 3D Printing
At its core, 3D printing represents a departure from traditional manufacturing methodologies. Instead of subtractive processes that involve cutting away from a solid block of material, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, using digital models to create three-dimensional structures. This additive approach offers unparalleled flexibility, precision, and customization in production.
Agility and Customization
One of the standout advantages of 3D printing in manufacturing is its agility. It enables rapid prototyping and iteration, allowing designers and engineers to test and refine designs swiftly.
This iterative approach significantly reduces lead times and accelerates the product development cycle, fostering a culture of continuous innovation. For a comprehensive understanding of these rapid prototyping capabilities, check out this website for a deeper dive into 3D printing’s role in accelerating product development.
Moreover, 3D printing facilitates customization on a scale previously unimaginable. The technology allows for the creation of intricate and highly personalized designs, catering to individual preferences without compromising efficiency.
This shift towards mass customization has redefined consumer expectations across industries, from healthcare to automotive and beyond.
Industry Applications
The impact of 3D printing spans a myriad of industries. In aerospace, where precision and lightweight components are paramount, 3D printing enables the production of intricate parts with reduced material waste. The technology’s ability to create complex geometries has transformed aircraft design and manufacturing, contributing to enhanced fuel efficiency and performance.
Similarly, in healthcare, 3D printing has revolutionized patient care. From prosthetics customized to fit individual needs to patient-specific implants and surgical models, the technology has elevated healthcare outcomes, offering tailored solutions that enhance both functionality and comfort.
Supply Chain Resilience and Sustainability
3D printing has also begun reshaping supply chains. The capacity for on-demand production reduces the need for large inventories, minimizing storage costs and the risks associated with overproduction or obsolete inventory. This agility in manufacturing contributes to a more resilient supply chain, capable of swiftly adapting to market fluctuations and demands.
Furthermore, sustainability is a key factor in the adoption of 3D printing. The technology’s ability to produce parts with less material waste, coupled with the potential for using recycled materials, aligns with the growing emphasis on eco-friendly manufacturing practices. Efforts to develop bio-based and recycled materials for 3D printing aim to further reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing processes.
Challenges and Innovations
Despite its many advantages, 3D printing in manufacturing faces challenges. Material limitations, such as strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness, remain focal points for research and development. Scientists and engineers continue to explore new materials that balance performance with sustainability and affordability.
Additionally, scalability and production speed are areas undergoing innovation. Advancements in printing speeds, larger-scale printing, and automation are enhancing the scalability of 3D printing, making it more viable for mass production.
The Future Landscape
Looking ahead, the trajectory of 3D printing in manufacturing is poised for continued growth and innovation. Advancements in materials science, software capabilities, and hardware development are expected to further expand the scope of 3D printing applications. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning is anticipated to optimize designs, predict performance outcomes, and enhance manufacturing processes.
Moreover, the democratization of 3D printing technologies, making them more accessible and user-friendly, will empower smaller enterprises and entrepreneurs to leverage the benefits of additive manufacturing, driving innovation and competitiveness across industries.
Rethinking Design and Complexity
The design freedom afforded by 3D printing is unparalleled. It enables the creation of highly complex geometries and intricate structures that were previously unattainable through conventional manufacturing methods.
Engineers and designers can now optimize parts for functionality, reducing the number of components and assembly processes. This not only streamlines manufacturing but also results in lighter, more durable, and often more efficient end products.
On-Demand Manufacturing and Inventory Management
Traditional manufacturing methods often necessitate large production runs to achieve economies of scale, leading to surplus inventory or the risk of stock obsolescence.
3D printing introduces the concept of on-demand manufacturing, allowing companies to produce parts and products only when needed. This mitigates inventory costs, reduces waste, and eliminates the need for extensive warehousing.
Additionally, distributed manufacturing becomes feasible with 3D printing. Parts can be produced closer to the point of use, reducing transportation needs and carbon footprints associated with long-distance shipping.
Enhancing Collaboration and Prototyping
The collaborative aspect of 3D printing is noteworthy. Design files can be easily shared and modified across geographical locations, fostering global collaboration. Prototyping becomes more efficient and cost-effective, enabling teams to iterate designs swiftly and improve products based on real-time feedback.
Moreover, the ability to create physical prototypes in-house reduces the reliance on external prototyping services, saving time and costs associated with outsourcing.
Empowering Small-Scale Production and Innovation
The accessibility of 3D printing technology has lowered the barriers to entry for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups. These entities can now compete with larger corporations by leveraging the capabilities of additive manufacturing. This democratization of technology fuels creativity and innovation, enabling smaller players to introduce unique and niche products to the market.
Challenges and Ongoing Developments
While 3D printing holds immense promise, challenges persist. Surface finish, material strength, and speed limitations in large-scale production remain areas of focus for further development. Improvements in post-processing techniques, advancements in material sciences, and innovations in printing technologies aim to address these challenges, making 3D printing more viable for a wider range of applications.
Future Innovations and Applications
Looking ahead, the future of 3D printing in manufacturing is rife with possibilities. Bioprinting for organ transplantation and tissue engineering, construction using 3D printed structures, and even the prospect of printing food are areas where ongoing research and experimentation promise groundbreaking innovations.
The integration of 3D printing with other emerging technologies, such as robotics and IoT, holds the potential to redefine smart manufacturing and create more autonomous and adaptive production processes.
As 3D printing technologies evolve and permeate various sectors, they continue to rewrite the rules of manufacturing. It’s not just about reshaping products; it’s about reimagining entire industries and paving the way for a future where imagination knows no limits and where the transformational potential of 3D printing in manufacturing continues to unfold.
Conclusion: A New Era of Manufacturing
In conclusion, 3D printing has ushered in a new era of manufacturing—a dynamic landscape characterized by innovation, customization, and sustainability. Its transformative power transcends traditional constraints, driving industries towards a future where the boundaries of what’s possible continue to expand.